
Old post detected!
This post is roughly 10 years old; originally published on April 16, 2014! The information presented here may be out of date and inaccurate.
Please read this page but do keep its age in mind.
I switched from BIP to ZNC, and recommend you use ZNC instead!
BIP is an IRC proxy that maintains a persistent connection(s) to a list of IRC channels. You can then point your IRC client to BIP each time you log in and playback the conversations that took place while you were away.
I’ve found bBIP to be so useful that I now maintain BIP for Arch Linux, although I now run my BIP proxy on Debian because my new VPS provider doesn’t offer Arch Linux as an option.
Installing BIP
Installing BIP is simple for both Arch Linux and Debian.
Debian
I run BIP on Debian Wheezy with the backport repository enabled.
sudo apt-get -t wheezy-backports install bip
sudo sed -i 's/ENABLED=0/ENABLED=1/' /etc/default/bip
Arch Linux
pacman -S bip
systemctl enable bip
Create a user
The next thing to do is create a username and password and BIP provides it’s
own utility for doing this called bipmkpw. Replace ‘username’ with whatever
you want your BIP ‘username’ to be. This name has no relation to any IRC
usernames so it can be anything.
bipmkpw username
Enter a password when prompted. The password will then be output as a hash. Make a note of both the hashed and un-hashed values somewhere, you will need them later.
Create a certificate
We don’t want the username and password being sent as clear-text, so we will create an SSL certificate for BIP to use.
openssl req -new -newkey rsa:4096 -nodes -x509 -keyout bip.pem -out bip.pem
Move the certificate to /var/lib/bip
sudo mv bip.pem /var/lib/bip
Change ownership and permissions of the certificate to the user bip which was
created automatically when the package was installed.
sudo chown bip:bip /var/lib/bip/bip.pem
sudo chmod 600 /var/lib/bip/bip.pem
Configure BIP
Here is example configuration for BIP. Copy it to /etc/bip.conf, modify it
accordingly and then change the ownership and permissions.
sudo chown bip:bip /etc/bip.conf
sudo chmod 640 /etc/bip.conf
Example configuration
# bip default config file.
# Thou shoult change thy password
ip = "0.0.0.0";
# To connect a client to bip, try the port below, and
# be sure to set the password to the value
# specified in the network you want to connect to.
port = 7778;
# If you set this to true, you'll only be able to connect to bip
# with a SSL capable IRC client. Be sure to generate a certificate
# for bip with 'make cert'
client_side_ssl = true;
log_level = 3;
pid_file="/var/run/bip/bip.pid";
# This is where logs go. Channel and private messages will use that
# configuration value as a prefix, and then log_format to determine
# full log filename.
log_root = "/var/log/bip/";
# Log format allows you to make log filenames depend on the log line's
# attributes. Here's a list :
# %u -> user name
# %n -> network name
# %Y -> 4 digit year
# %m -> 2 digit month
# %d -> 2 digit day
# %c -> destination (#chan, privates, ...)
#log_format = "%n/%Y-%m/%c.%d.log";
# Sets the frequency (in seconds) of log syncing (real write to kernel)
#log_sync_interval = 5;
# Makes bip send the log of each channel and privates while
# you were not connected to the proxy upon connection.
backlog = true; # enable backlog
backlog_lines = 0; # number of lines in backlog, 0 means no limit
backlog_always = false; # backlog even lines already backlogged
# If blreset_on_talk talking on an irc network has the same effect of issuing
# /bip blreset, meaning that stuffed logged before the command won't be read
# back on backlog
blreset_on_talk = true;
# Network definition, a name and server info
network {
name = "freenode";
server { host = "chat.freenode.net"; port = 6667; };
};
network {
name = "blitzed";
server { host = "irc.blitzed.org"; port = 6667; };
};
# Configuration example with one user who connects to two irc networks
# To use the multi-server feature:
# - define the connections
# - chose and setup a different login for each connection
# on your irc client:
# - Use the multi server feature of your client, the server being each time
# the server where bip is running. In your client setup server password to:
# username:password:connectionname
# - do not store the password in clear here, use the bipmkpw util to generate
# a hash
# User structure is grouping information for a given user
user {
# The name in bip of the user
# This is used by bip only
name = "USERNAME; #BIP User account created with bipmkpw
password = "00000000000000000000000000000000000000"; # the hash bipmkpw created
ssl_check_mode = "none";
# These will be the default for each connections
default_nick = "NICKNAME"; #IRC Nick
default_user = "IRCUSERNAME"; #IRC User
default_realname = "REALNAME"; #IRC Real Name
admin = true;
backlog_msg_only = true; # When true,
# A user can have mutiple connections to irc networks.
# define a connection:
connection {
name = "freenode"; # used by bip only
network = "freenode"; # which ircnet to connect to
# these will be sent to the real IRC server
user = "IRCUSERNAME";
realname = "IRCREALNAME";
password = "serverpassword"; #can be commented out if not needed
# Some options:
follow_nick = true;
ignore_first_nick = false;
#on_connect_send = "PRIVMSG NickServ :IDENTIFY nspassword";
# Autojoined channels:
channel { name = "#cat"; }; # Join #cat
channel { name = "#dog"; backlog = false; }; # Join #dog but don't backlog it.
channel { name = "#pig"; key = "01nk01nk"; }; # Join #pig that has a password.
};
connection {
name = "blitzed"; # used by bip only
network = "blitzed"; # which ircnet to connect to
# these will be sent to the real IRC server
user = "IRCUSERNAME";
realname = "IRCREALNAME";
password = "serverpassword"; #can be commented out if not needed
# Some options:
follow_nick = true;
ignore_first_nick = false;
#on_connect_send = "PRIVMSG NickServ :IDENTIFY nspassword";
# Autojoined channels:
channel { name = "#bar"; };
channel { name = "#foo"; };
};
};
If you require any clarification about what the configuration options do then
man bip.conf is your friend.
Start BIP
Now that BIP is configured, it can be started.
Debian
sudo /etc/init.d/bip start
Arch Linux
sudo systemctl start bip
Client configuration
I use HexChat, but other IRC clients are available.
I add a new Network to HexChat for each of the IRC networks I defined in
/etc/bip.conf. The screen shot below shows how I configure a BIP network in
HexChat.
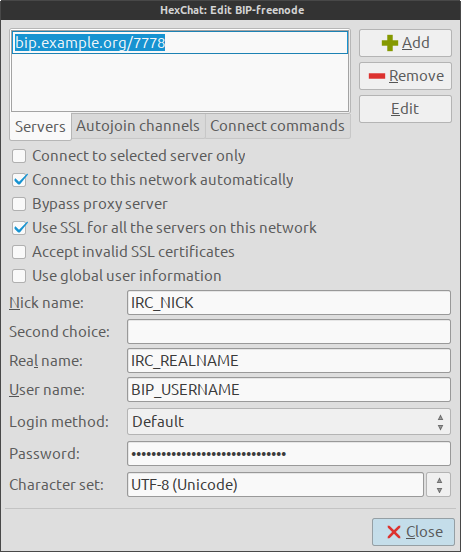
Password format
The Password is the most important and confusing item. This is for BIP, not for any IRC network. Remember the unhashed password? That goes here but with a twist. The format for the password is:
bipusername:unhashedbippassword:bipnetwork
Bipnetwork? What is that? It is from the following section of /etc/bip.conf
on the server?
network {
name = "freenode";
server { host = "chat.freenode.net"; port = 6667; };
};
A more practical example:
myuser:S3cr3tP@$$w0rd:freenode
Conclusion
And that’s it! We are now perpetually connected to IRC, can connect to BIP proxy from multiple devices in a completely transparent and seamless manner. Moreover, the logs for all channels are saved and automatically rotated on the server.
If you looking for an alternative to BIP, then try ZNC.
References